The Dawn of Log Video Formats
In the early days of digital video, data storage and processing power were limited.
This led to the development of log video formats, which helped to efficiently represent a wide range of luminance values.
The Introduction of Cineon
In 1992, Kodak introduced the Cineon digital film system. This groundbreaking technology allowed filmmakers to scan and digitally manipulate film negatives.
The Cineon format used logarithmic encoding to preserve the full dynamic range of film.
The Arrival of S-Log
Sony revolutionized the industry in 2003 with the release of their S-Log gamma curve.
S-Log is designed for Sony's digital cinema cameras and offers a wide dynamic range, enabling cinematographers to capture more details in shadows and highlights.

The Expansion of Log Formats
Over the years, other manufacturers developed their own log formats. Some notable examples include:
- Canon's C-Log
- Panasonic's V-Log
- RED's REDLogFilm
- Blackmagic Design's BMD Film
Each format has its unique characteristics and caters to different camera systems and workflows.
The Rise of HDR and Log Video
High Dynamic Range (HDR) content started gaining popularity in the early 2010s.
HDR allows for a greater range of luminance levels, resulting in more realistic and vibrant images. The use of log video formats is essential in capturing the necessary data for HDR workflows.
The Standardization of Log Video Formats
As log video formats continued to evolve, the need for standardization became evident. In 2016, the Academy Color Encoding System (ACES) was introduced, aiming to provide a unified color management framework for the industry.
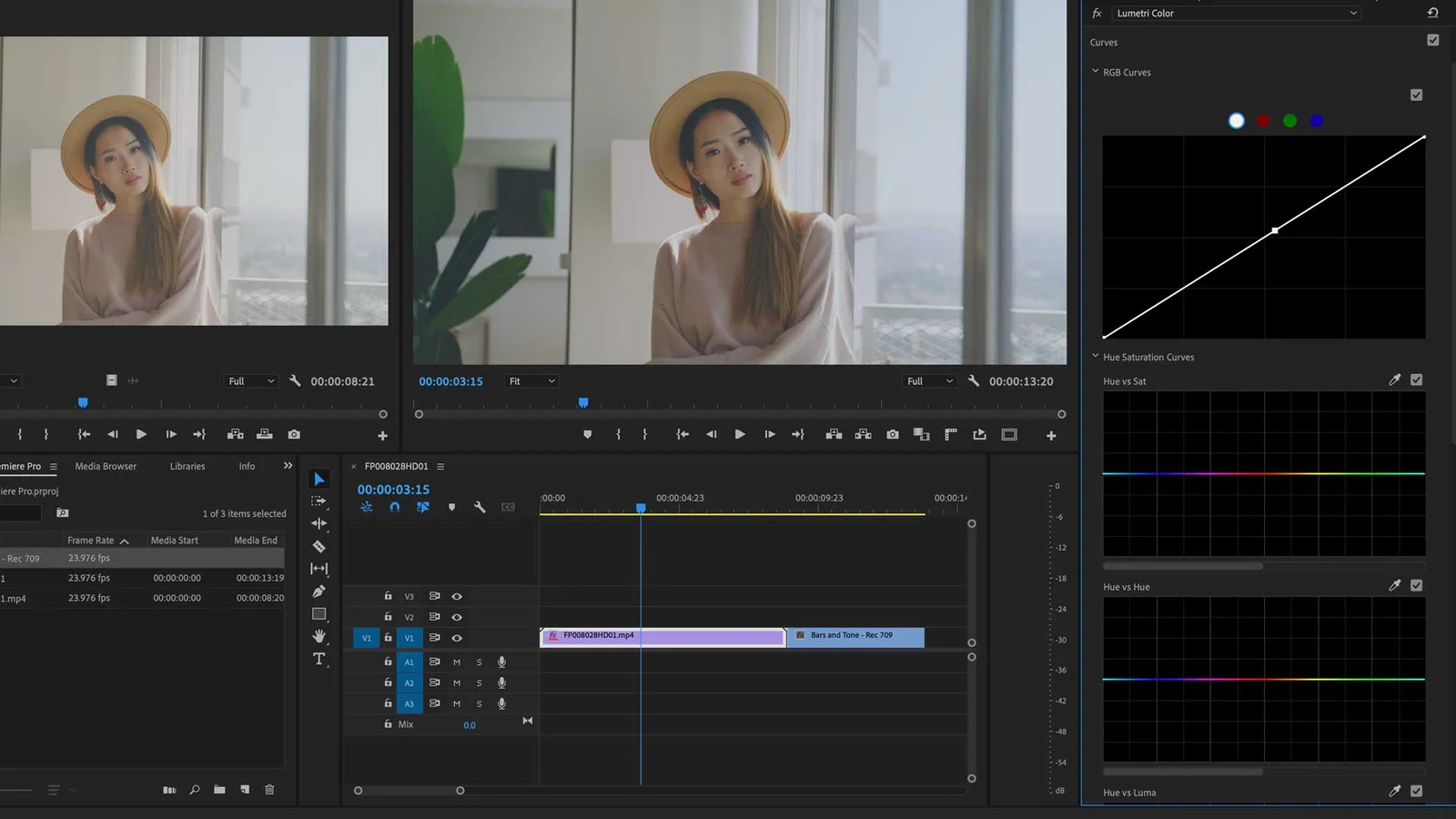
Log Video Formats and Color Grading
Color grading plays a crucial role in the post-production process, enabling filmmakers to enhance the visual aesthetic of their projects.
Log video formats offer increased flexibility in color grading, allowing for more creative freedom and precise adjustments.
The Future of Log Video Formats
As technology advances, log video formats will continue to adapt and improve. Emerging trends, such as virtual production and real-time ray tracing, will likely drive further developments in this area.

History of Log Video Formats Frequently Asked Questions
What is a log video format?
A log video format is a method of encoding video data that uses logarithmic encoding to preserve a wider dynamic range, capturing more details in shadows and highlights.
Why are log video formats important in filmmaking?
Log video formats enable filmmakers to capture a wider dynamic range and preserve more detail in their footage. This provides greater flexibility in post-production, particularly during color grading.
What is the difference between S-Log, C-Log, and V-Log?
S-Log, C-Log, and V-Log are log video formats developed by Sony, Canon, and Panasonic, respectively. Each format has unique characteristics, and they are tailored to the specific camera systems and workflows of each manufacturer.
How does HDR relate to log video formats?
HDR (High Dynamic Range) content requires a wider dynamic range than traditional video. Log video formats are essential for capturing the necessary data for HDR workflows.
What is the Academy Color Encoding System (ACES)?
ACES is a standardized color management framework introduced in 2016. It aims to provide a unified system for the industry, simplifying workflows and ensuring consistent color reproduction across different devices and platforms.
Can I use log video formats with any camera?
Not all cameras support log video formats. Typically, log formats are available in higher-end cinema cameras and some professional mirrorless or DSLR cameras.
What is color grading, and why is it important?
Color grading is the process of adjusting the colors and tones in video footage to enhance its visual aesthetic and create a specific mood or look. It is a crucial step in post-production that allows filmmakers to shape the final appearance of their projects and ensure visual consistency.
How do I choose the right log video format for my project?
Choosing the right log video format depends on your camera system and workflow requirements. Research the available log formats for your camera and consider factors such as dynamic range, color accuracy, and compatibility with your post-production tools.
Can I shoot in a log format and not color grade my footage?
Shooting in a log format without color grading is not recommended, as log footage typically appears flat and desaturated. Color grading is necessary to bring out the intended colors, contrast, and overall visual aesthetic.
Are there any downsides to using log video formats?
While log video formats offer many benefits, they may also require more storage space, increased processing power in post-production, and a more advanced understanding of color grading techniques.

About the Author
Joseph Nilo has been working professionally in all aspects of audio and video production for over twenty years. His day-to-day work finds him working as a video editor, 2D and 3D motion graphics designer, voiceover artist and audio engineer, and colorist for corporate projects and feature films.
Parent Article:
Log Video Formats Reference Guide
Related Articles:
The Evolution of Log Video Formats
Demystifying Log Video Formats
Log Video Formats vs. Traditional Video Formats
Top 10 Log Video Format Cameras
Color Grading Techniques for Log Video Formats
The Impact of Log Video Formats on Modern Cinematography
Mastering Post-Production Workflows for Log Video Formats
Best Practices for Archiving and Storing Log Video Format Files
Video Editing Related Posts
Adobe Creative Cloud for Video Editing
Top 10 Video Editing Software for Mac
The Benefits of Dual-Monitor Setups for Video Editing
How to Choose the Right Video Editing Monitor for Your Needs
Best Monitors for Video Editing
Best Video Editing Software in 2023
Best Mac for Video Editing in 2023
(Almost) 50 Mistakes Every New Video Producer Makes
Breakthrough AI Tools: Elevate Your Video Production Game!
- The Dawn Of Log Video Formats
- The Introduction Of Cineon
- The Arrival Of S-Log
- The Expansion Of Log Formats
- The Rise Of HDR And Log Video
- Standardization Of Log Video Formats
- Log Video Formats And Color Grading
- Future Of Log Video Formats
- History Of Log Video Formats FAQ
Parent Article:
Log Video Formats Reference Guide
Related Articles:
The Evolution of Log Video Formats
Demystifying Log Video Formats
Log Video Formats vs. Traditional Video Formats
Top 10 Log Video Format Cameras
Color Grading Techniques for Log Video Formats
The Impact of Log Video Formats on Modern Cinematography
Mastering Post-Production Workflows for Log Video Formats
Best Practices for Archiving and Storing Log Video Format Files
Video Editing Related Posts
Adobe Creative Cloud for Video Editing
Top 10 Video Editing Software for Mac
The Benefits of Dual-Monitor Setups for Video Editing
How to Choose the Right Video Editing Monitor for Your Needs
Best Monitors for Video Editing
Best Video Editing Software in 2023
Best Mac for Video Editing in 2023
(Almost) 50 Mistakes Every New Video Producer Makes
Breakthrough AI Tools: Elevate Your Video Production Game!
