Adobe Media Encoder is a gem in the suite of Adobe applications.
It stands as an important tool for anyone looking to process their media files efficiently.
Whether it’s converting file formats, compressing files, or preparing media for the web, this tool is your go-to.
So, let's dive deep into how to use Adobe Media Encoder effectively.
This page may include affiliate links.
Though I only recommend software that I use and fully believe in.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
I pay for Adobe Creative Cloud and have used it every day in my 20-year career as a video editor, producer, and colorist.
Purchasing Adobe CC through these links will get you the best deal available and support this site.
Get Adobe Creative Cloud Now!Table of Contents
- Getting Your Feet Wet: Setting Up Adobe Media Encoder
- Adobe Media Encoder System Requirements
- Importing Media: The First Step To Processing
- Export Settings: Tailoring Your Output
- Preset Browser: Your Encoding Companion
- The Encoding Queue: Where The Magic Happens
- Adobe Media Encoder Supported File Formats
- Common Pitfalls And How To Avoid Them
- Adobe Media Encoder FAQ:
Getting Your Feet Wet: Setting Up Adobe Media Encoder
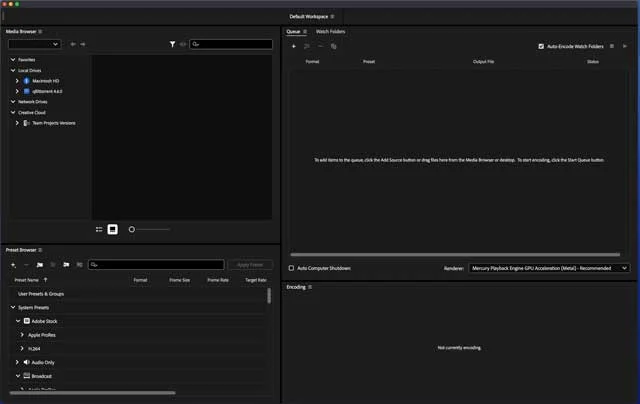
Adobe Media Encoder (AME) is user-friendly, but a well-structured setup can save you a ton of time in the long run.
First things first, ensure your system meets the required specifications to run the application smoothly.
Once installed, familiarize yourself with the workspace layout.
It’s intuitive with panels such as Queue, Preset Browser, and the Encoding panel.
Adobe Media Encoder System Requirements
| Specification | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Operating System | Windows 10 (64-bit) or macOS X v10.13 or later |
| Processor | Multicore processor with 64-bit support |
| RAM | 8 GB (16 GB or more recommended) |
| Hard Disk Space | 4 GB of available hard-disk space; additional free space required during installation |
| Graphics | Adobe-recommended GPU card for GPU-accelerated performance |
| Internet | Internet connection and registration are necessary for required software activation, validation of subscriptions, and access to online services |
Importing Media: The First Step to Processing
Importing media is straightforward.
Click on the “+” button in the queue panel or drag your media file into the panel. AME supports a wide range of file formats, making it a versatile choice for different media types.
Export Settings: Tailoring Your Output
Before hitting the encode button, you need to specify your export settings.
This is where you decide the file format, bitrate, resolution, and other parameters.
The right settings ensure your media is optimized for its intended use.
Preset Browser: Your Encoding Companion
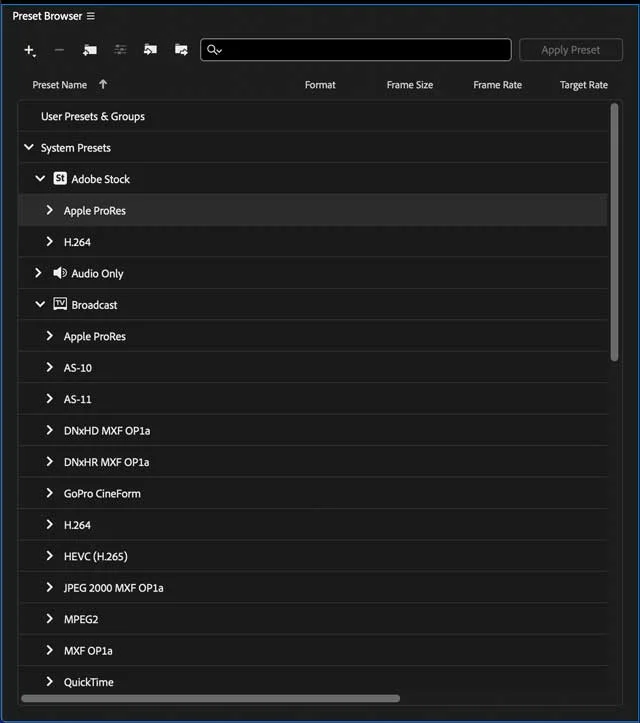
The Preset Browser is where AME shines.
It houses a multitude of presets for different output requirements.
Whether you are exporting for YouTube, Vimeo, or any other platform, there's likely a preset that matches your needs.
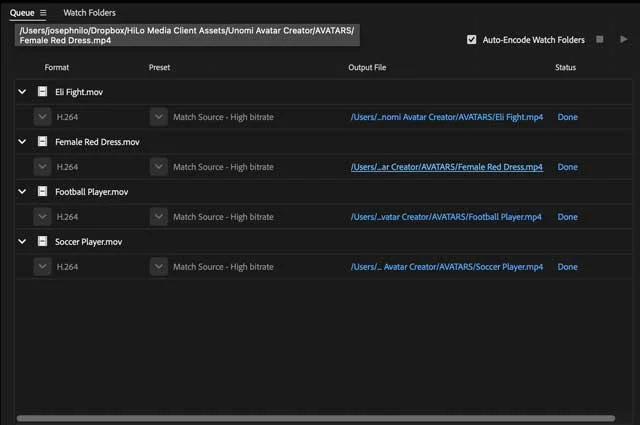
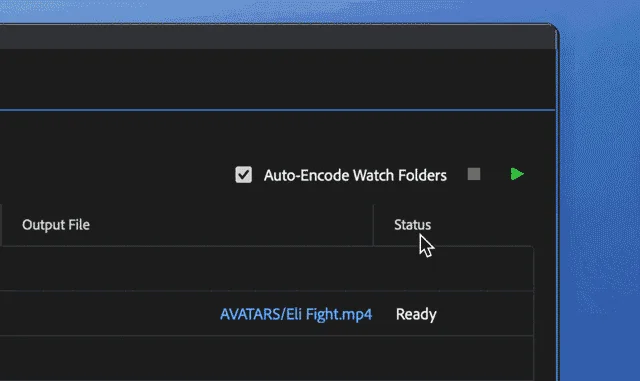
The Encoding Queue: Where the Magic Happens
Once your media is in the queue with the desired settings, hit the green play button. Watch as AME efficiently processes your media, readying it for upload or further editing.
Adobe Media Encoder Supported File Formats
| File Type | File Extension |
|---|---|
| Video Formats | .mp4, .mov, .avi, .mkv, .mpeg, .webm |
| Audio Formats | .mp3, .wav, .aac, .ac3 |
| Image Formats | .jpg, .png, .gif, .bmp, .tiff |
| Other Formats | .vob, .mxf, .flv, .swf |
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
While AME is powerful, common issues like error messages during encoding or unexpected output quality can arise.
Most errors stem from incorrect settings or unsupported file formats.
Ensure your settings match your output requirements and your files are in supported formats.
Adobe Media Encoder FAQ:
How Can I Speed Up Encoding in Adobe Media Encoder?
Optimize your settings, particularly the resolution and bitrate. Also, closing other running applications frees up resources for AME.
What File Formats Does Adobe Media Encoder Support?
Adobe Media Encoder supports a vast array of file formats including MP4, MOV, AVI, and more. A detailed list can be found on Adobe’s official website.
Can I Batch Process Multiple Files?
Absolutely! Batch processing is one of the core benefits of using Adobe Media Encoder. Simply add all your files to the queue, specify the settings, and hit encode.

About the Author
Joseph Nilo has been working professionally in all aspects of audio and video production for over twenty years. His day-to-day work finds him working as a video editor, 2D and 3D motion graphics designer, voiceover artist and audio engineer, and colorist for corporate projects and feature films.
Related Posts:
Adobe Creative Cloud What Is Series
Adobe Creative Cloud Pricing Explained
Adobe Creative Cloud Pricing and Plans - The Ultimate Resource
Best Adobe Creative Cloud Apps for Graphic Design
How to Install Adobe Creative Cloud on Mac
Adobe Creative Cloud for Photographers
Adobe Creative Cloud for Video Editing
How to Use Adobe Creative Cloud Libraries
Adobe Creative Cloud Subscription Discount
Video Encoding Related Posts:
What is the Best Target Bitrate for YouTube?
Best Premiere Pro Export Settings for YouTube
High Bitrate vs. Adaptive High Bitrate
How to use SurferSEO to Write Scripts for YouTube Videos
Best Microphones For YouTube Videos 2022
Best Mac for Video Editing in 2023
Best Monitors for Video Editing
Find the Best Export Settings for YouTube Videos Now!
Mastering Adobe Media Encoder: Your Gateway to Efficient Media Processing
Video Editing Related Posts
Adobe Creative Cloud for Video Editing
Top 10 Video Editing Software for Mac
The Benefits of Dual-Monitor Setups for Video Editing
How to Choose the Right Video Editing Monitor for Your Needs
Best Monitors for Video Editing
Best Video Editing Software in 2023
Best Mac for Video Editing in 2023
(Almost) 50 Mistakes Every New Video Producer Makes
Breakthrough AI Tools: Elevate Your Video Production Game!
- Getting Your Feet Wet: Setting Up Adobe Media Encoder
- Adobe Media Encoder System Requirements
- Importing Media: The First Step To Processing
- Export Settings: Tailoring Your Output
- Preset Browser: Your Encoding Companion
- The Encoding Queue: Where The Magic Happens
- Adobe Media Encoder Supported File Formats
- Common Pitfalls And How To Avoid Them
- Adobe Media Encoder FAQ:
Related Posts:
Adobe Creative Cloud What Is Series
Adobe Creative Cloud Pricing Explained
Adobe Creative Cloud Pricing and Plans - The Ultimate Resource
Best Adobe Creative Cloud Apps for Graphic Design
How to Install Adobe Creative Cloud on Mac
Adobe Creative Cloud for Photographers
Adobe Creative Cloud for Video Editing
How to Use Adobe Creative Cloud Libraries
Adobe Creative Cloud Subscription Discount
Video Encoding Related Posts:
What is the Best Target Bitrate for YouTube?
Best Premiere Pro Export Settings for YouTube
High Bitrate vs. Adaptive High Bitrate
How to use SurferSEO to Write Scripts for YouTube Videos
Best Microphones For YouTube Videos 2022
Best Mac for Video Editing in 2023
Best Monitors for Video Editing
Find the Best Export Settings for YouTube Videos Now!
Mastering Adobe Media Encoder: Your Gateway to Efficient Media Processing
Video Editing Related Posts
Adobe Creative Cloud for Video Editing
Top 10 Video Editing Software for Mac
The Benefits of Dual-Monitor Setups for Video Editing
How to Choose the Right Video Editing Monitor for Your Needs
Best Monitors for Video Editing
Best Video Editing Software in 2023
Best Mac for Video Editing in 2023
(Almost) 50 Mistakes Every New Video Producer Makes
Breakthrough AI Tools: Elevate Your Video Production Game!
